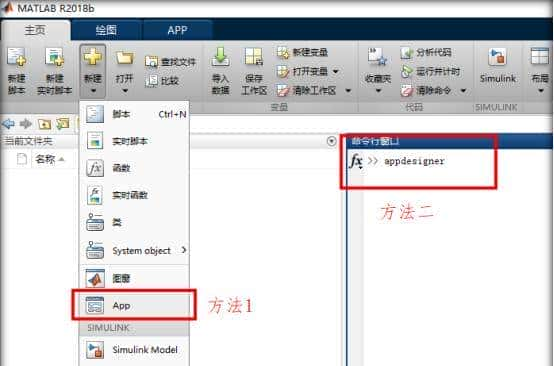
海外百战系列针对想海外求职的顶尖算法和量化程序员
🌐 HTTP AND HTTPS: AN INTRODUCTION AND COMPARISON
Here is a full English explanation of HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure), two fundamental protocols for transmitting data on the internet. Their crucial difference lies in security.
💻 1. HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
HTTP is the foundational protocol used to retrieve resources such as HTML pages, image files, and query results from a web server.
Key Features:
Port: Default port is 80.Security: Non-secure. Data is transmitted across the network in plain text.Connection: Stateless (the server does not remember the state of previous requests).Performance: Lower protocol overhead, generally faster transmission (but at high security risk).Encryption: None.
Risk Warning: Because HTTP transmits data in plain text, any intermediary (like an ISP or a network eavesdropper) can easily intercept and read the content being transmitted, including sensitive data such as passwords and credit card information.
🔒 2. HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure)
HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP. It achieves encrypted data transfer by inserting the TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer) protocol between HTTP and TCP.
Key Features:
Port: Default port is 443.Security: Secure. Data is encrypted before sending and decrypted only upon reception.Core Mechanism: Relies on the TLS/SSL protocol.Authentication: Typically requires the server to possess a Digital Certificate issued by a Certificate Authority, which is used to verify the server’s identity and prevent phishing attacks.Encryption: Uses Hybrid Encryption:
Asymmetric Encryption: Used during the handshake to securely exchange the session key.Symmetric Encryption: Used for the actual data transfer, which is much more efficient.
📊 3. Comparison Summary
| Feature | HTTP | HTTPS |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | HyperText Transfer Protocol | HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure |
| Security | Plain text, non-secure | Encrypted via TLS/SSL, secure |
| Default Port | 80 | 443 |
| Required Certificate | None | Requires an SSL/TLS Certificate |
| Security Process | None | Data encryption, Identity verification, Data integrity check |
| Speed/Overhead | Faster, low overhead | Slightly slower (due to encryption/decryption), but negligible impact with modern hardware |
🎯 Significance for Algorithm and Quant Programmers
For engineers building high-performance, high-security systems:
Security: When handling sensitive user data (e.g., transaction details, API Keys), HTTPS is mandatory to prevent Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks.Performance: Although HTTPS introduces overhead for handshake and encryption, modern hardware and protocol optimizations (such as TLS 1.3 and HTTP/2) have significantly reduced latency. In system design, you must weigh security against minor performance costs.Certificate Management: Understanding the processes of issuance, renewal, and revocation of certificates is a critical part of maintaining stable online services.
相关文章