【u-boot】u-boot网络系统剖析
本文基于u-boot源码版本:
v2017.09
一、网络系统
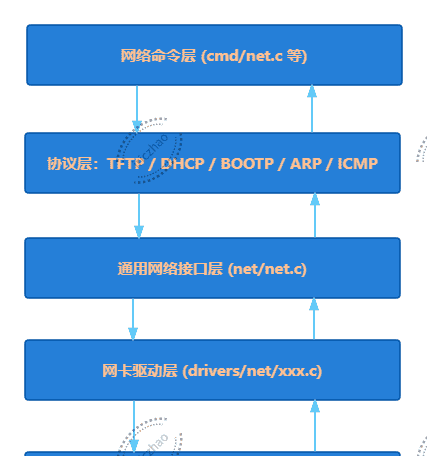
u-boot网络系统分为四类:
(1)网络驱动: 位于
drivers/net/
(2)网络核心框架:实现了数据包的接收分发机制;实现了网络状态机(通过
net_state
(3)网络协议层:实现u-boot支持网络的协议,位于
net/
(4)网络命令层:实现u-boot网络命令的文件,位于
cmd/
(1-1)网络驱动
位于
drivers/net/
struct eth_ops
struct eth_ops {
/* 准备硬件以便进行数据包的发送和接收。 */
int (*start)(struct udevice *dev);
/* 将传入的 “packet” 缓冲区中的字节作为一个网络数据包发送出去。 */
int (*send)(struct udevice *dev, void *packet, int length);
/*
* 检查硬件是否接收到数据包。如果接收到,则通过参数 packetp
* 返回指向数据包缓冲区的指针;如果没有接收到,则返回错误码或0。
* 返回0表示硬件接收FIFO为空。若返回0,网络栈不会处理空包,
* 但如果定义了free_pkt(),该函数仍会被调用以释放包内存。
*/
int (*recv)(struct udevice *dev, int flags, uchar **packetp);
/*
* 当网络栈处理完数据包后,驱动可借此机会管理其包缓冲区内存。
* 仅当 recv 没有返回错误时才会调用此函数 —— 可选实现。
*/
int (*free_pkt)(struct udevice *dev, uchar *packet, int length);
/* 停止硬件的包检测操作,即使当前状态为PASSIVE时也可能被调用。 */
void (*stop)(struct udevice *dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_MCAST_TFTP
/* 加入或离开一个多播组(用于 TFTP 等)—— 可选实现 */
int (*mcast)(struct udevice *dev, const u8 *enetaddr, int join);
#endif
/*
* 将MAC地址写入硬件(在部分平台如ARM上用于传递给linux)。
* 此函数期望eth_pdata::enetaddr字段已被填充。
* 若返回-ENOSYS,表示该硬件不支持此功能 —— 可选实现。
*/
int (*write_hwaddr)(struct udevice *dev);
/*
* 某些设备在板载 ROM 中保存有备用 MAC 地址。
* 驱动应通过此函数将该地址提供给网络栈。
* 函数应填写eth_pdata::enetaddr字段——可选实现。
*/
int (*read_rom_hwaddr)(struct udevice *dev);
};
常见驱动有:
stmmac.c
fec_mxc.c
bcm_eth.c
rtl8169.c
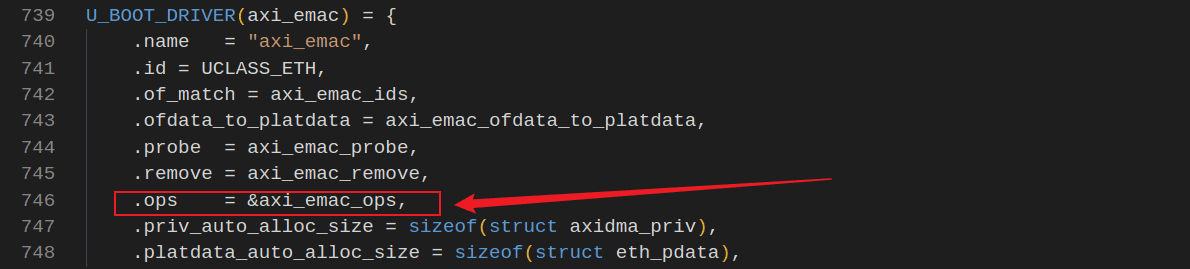
例如xilinx_axi_emac.c文件中的驱动描述,首先创建静态
struct eth_ops
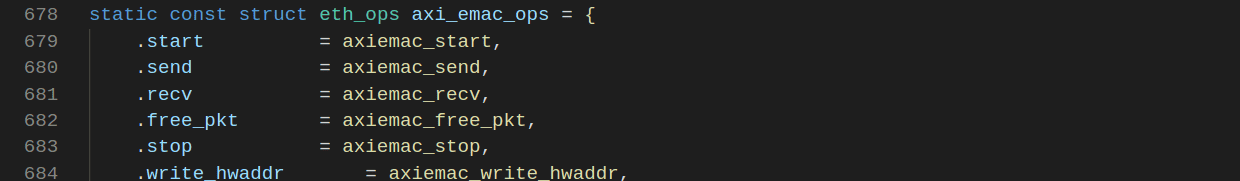
使用
U_BOOT_DRIVER()
.ops
(1-2)网络核心框架
net/net.c
实现了数据包的接收分发机制;实现了网络状态机(通过
net_state
主要函数如下:
int net_init(void);
int net_loop(enum proto_t protocol); //启动网络通信
void net_receive(uchar *pkt, int len); //收包分发
void net_send_packet(uchar *pkt, int len);
net_loop()
(1-3)网络协议层
网络协议层位于
net/
| 协议 | 源文件 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| ARP | |
实现MAC地址与IP地址的映射 |
| BOOTP/DHCP | |
动态获取IP地址及网络参数 |
| ICMP | |
实现ping命令 |
| TFTP | |
通过TFTP下载镜像文件 |
| NFS | |
通过NFS挂载加载文件 |
| DNS | |
支持主机名解析 |
(1-4)网络命令层
网路命令层位于
cmd/
| 命令 | 源文件 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
测试网络连通性 |
|
|
通过DHCP获取IP |
|
|
通过TFTP下载镜像 |
|
|
从NFS下载镜像 |
二、初始化
(2-1)网络系统初始化
在u-boot启动路径中,使用
initr_net()
static int initr_net(void)
{
puts("Net: ");
eth_initialize();
#if defined(CONFIG_RESET_PHY_R)
debug("Reset Ethernet PHY
");
reset_phy();
#endif
return 0;
}
eth_initialize()
int eth_initialize(void)
{
int num_devices = 0;
struct udevice *dev;
eth_common_init();
/*
* Devices need to write the hwaddr even if not started so that Linux
* will have access to the hwaddr that u-boot stored for the device.
* This is accomplished by attempting to probe each device and calling
* their write_hwaddr() operation.
*/
uclass_first_device(UCLASS_ETH, &dev);
if (!dev) {
printf("No ethernet found.
");
bootstage_error(BOOTSTAGE_ID_NET_ETH_START);
} else {
char *ethprime = env_get("ethprime");
struct udevice *prime_dev = NULL;
if (ethprime)
prime_dev = eth_get_dev_by_name(ethprime);
if (prime_dev) {
eth_set_dev(prime_dev);
eth_current_changed();
} else {
eth_set_dev(NULL);
}
bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_NET_ETH_INIT);
do {
if (num_devices)
printf(", ");
printf("eth%d: %s", dev->seq, dev->name);
if (ethprime && dev == prime_dev)
printf(" [PRIME]");
eth_write_hwaddr(dev);
uclass_next_device(&dev);
num_devices++;
} while (dev);
putc('
');
}
return num_devices;
}
eth_initialize()
调用通用网络初始化
eth_common_init()
UCLASS_ETH
ethprime
eth_write_hwaddr(dev)
(2-2)命令网络初始化
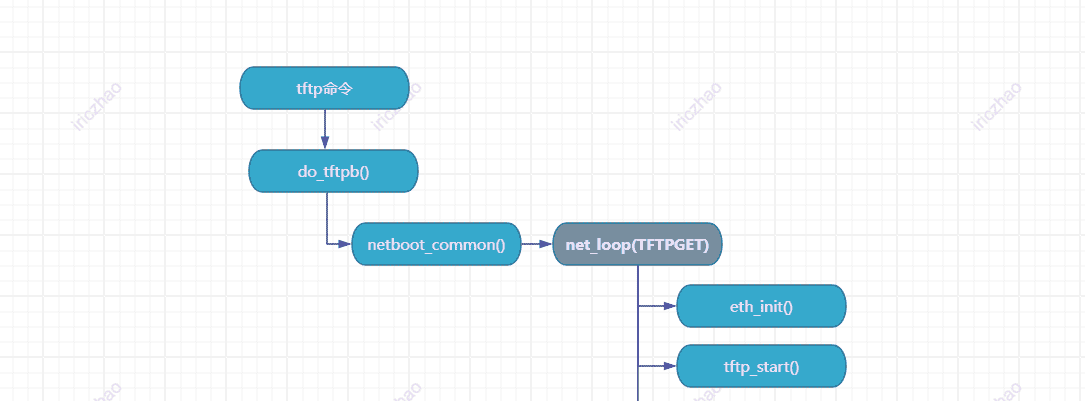
例如当执行以下命令时:
tftpboot 0x82000000 uImage
上述命令内部调用链大致如下:
三、网络处理循环分析
u-boot网络相关命令将触发
net_loop()
int net_loop(enum proto_t protocol)
{
int ret = -EINVAL;
net_restarted = 0;
net_dev_exists = 0;
net_try_count = 1;
debug_cond(DEBUG_INT_STATE, "--- net_loop Entry
");
bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_ETH_START, "eth_start");
/* 网络全局初始化 */
net_init();
/*
* 按需初始化网卡或只初始化state(eth_on_demand/NETCONS特殊处理)
*/
if (eth_is_on_demand_init() || protocol != NETCONS) {
eth_halt();
eth_set_current();
ret = eth_init();
if (ret < 0) {
eth_halt();
return ret;
}
} else {
eth_init_state_only();
}
restart:
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_KEYBOARD
net_busy_flag = 0;
#endif
net_set_state(NETLOOP_CONTINUE);
/*
* Start the ball rolling with the given start function. From
* here on, this code is a state machine driven by received
* packets and timer events.
*/
debug_cond(DEBUG_INT_STATE, "--- net_loop Init
");
/* 设置循环相关的 timer/handler 初始值 */
net_init_loop();
/*
* 检查前置条件并返回:
* 1:网络未配置(例如 IP 未设或 DHCP 不可用)→ 停止并返回 -ENODEV。
* 2:网络设备未配置(可能是eth未选定)→ 继续(但不设置net_dev_exists)。
* 0:预备就绪,设置net_dev_exists = 1,并根据protocol触发对
* 应的启动函数(如tftp_start()、dhcp_request() etc.)。
*/
switch (net_check_prereq(protocol)) {
case 1:
/* network not configured */
eth_halt();
return -ENODEV;
case 2:
/* network device not configured */
break;
case 0:
net_dev_exists = 1;
net_boot_file_size = 0;
/* 根据protocol调用对应的start函数,例如tftp_start, dhcp_request等 */
switch (protocol) {
case TFTPGET:
#ifdef CONFIG_CMD_TFTPPUT
case TFTPPUT:
#endif
/* always use ARP to get server ethernet address */
tftp_start(protocol);
break;
#ifdef CONFIG_CMD_TFTPSRV
case TFTPSRV:
tftp_start_server();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_DHCP)
case DHCP:
bootp_reset();
net_ip.s_addr = 0;
dhcp_request(); /* Basically same as BOOTP */
break;
#endif
case BOOTP:
bootp_reset();
net_ip.s_addr = 0;
bootp_request();
break;
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_RARP)
case RARP:
rarp_try = 0;
net_ip.s_addr = 0;
rarp_request();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_PING)
case PING:
ping_start();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_NFS)
case NFS:
nfs_start();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_CDP)
case CDP:
cdp_start();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_NETCONSOLE) && !defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD)
case NETCONS:
nc_start();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_SNTP)
case SNTP:
sntp_start();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_DNS)
case DNS:
dns_start();
break;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_LINK_LOCAL)
case LINKLOCAL:
link_local_start();
break;
#endif
default:
break;
}
break;
}
#if defined(CONFIG_MII) || defined(CONFIG_CMD_MII)
#if defined(CONFIG_SYS_FAULT_ECHO_LINK_DOWN) &&
defined(CONFIG_LED_STATUS) &&
defined(CONFIG_LED_STATUS_RED)
/*
* Echo the inverted link state to the fault LED.
*/
if (miiphy_link(eth_get_dev()->name, CONFIG_SYS_FAULT_MII_ADDR))
status_led_set(CONFIG_LED_STATUS_RED, CONFIG_LED_STATUS_OFF);
else
status_led_set(CONFIG_LED_STATUS_RED, CONFIG_LED_STATUS_ON);
#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_FAULT_ECHO_LINK_DOWN, ... */
#endif /* CONFIG_MII, ... */
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_KEYBOARD
net_busy_flag = 1;
#endif
/*
* 主数据包接收循环。
* 持续循环接收数据包,直到将net_state设置为某个终止状态为止。
*/
for (;;) {
WATCHDOG_RESET(); /* 喂狗,防止看门狗重启。 */
#ifdef CONFIG_SHOW_ACTIVITY
show_activity(1);
#endif
/*
* arp_timeout_check() 若返回>0,说明 ARP 有相关时间调整,重置 time_start 确保定时器同步。
*/
if (arp_timeout_check() > 0)
time_start = get_timer(0);
/* 【源码注释】
* 检查以太网是否有新数据包。
* 以太网的接收例程将对其进行处理。
* 大多数驱动程序会返回最近一次接收到的数据包大小,
* 但不会返回可能发生的错误信息。
*/
/*
* 调用驱动层接收方法,驱动会在接收到包时调用net层的回调来处
* 理(如将包分发给tftp/dhcp/arp handler)。这是触发state变化和数据传输的主要途径。
* 注意:eth_rx()是非阻塞地调用(多数驱动返回空或包大小),但驱动实现若阻塞会影响循环。
*/
eth_rx();
/*
* Abort if ctrl-c was pressed.
*/
if (ctrlc()) {
/* cancel any ARP that may not have completed */
net_arp_wait_packet_ip.s_addr = 0;
net_cleanup_loop();
eth_halt();
/* Invalidate the last protocol */
eth_set_last_protocol(BOOTP);
puts("
Abort
");
/* include a debug print as well incase the debug
messages are directed to stderr */
debug_cond(DEBUG_INT_STATE, "--- net_loop Abort!
");
ret = -EINTR;
goto done;
}
/*
* Check for a timeout, and run the timeout handler
* if we have one.
*/
if (time_handler &&
((get_timer(0) - time_start) > time_delta)) {
thand_f *x;
#if defined(CONFIG_MII) || defined(CONFIG_CMD_MII)
#if defined(CONFIG_SYS_FAULT_ECHO_LINK_DOWN) &&
defined(CONFIG_LED_STATUS) &&
defined(CONFIG_LED_STATUS_RED)
/*
* Echo the inverted link state to the fault LED.
*/
if (miiphy_link(eth_get_dev()->name,
CONFIG_SYS_FAULT_MII_ADDR))
status_led_set(CONFIG_LED_STATUS_RED,
CONFIG_LED_STATUS_OFF);
else
status_led_set(CONFIG_LED_STATUS_RED,
CONFIG_LED_STATUS_ON);
#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_FAULT_ECHO_LINK_DOWN, ... */
#endif /* CONFIG_MII, ... */
debug_cond(DEBUG_INT_STATE, "--- net_loop timeout
");
x = time_handler;
time_handler = (thand_f *)0;
(*x)();
}
/* 在失败状态下可能进行重新启动策略(如切换网口或增大重试计数) */
if (net_state == NETLOOP_FAIL)
ret = net_start_again();
/*
* 【状态机处理】
*/
switch (net_state) {
case NETLOOP_RESTART: /* 设置net_restarted后跳到restart标签,重新进行初始化/启动(这个是可循环的)。*/
net_restarted = 1;
goto restart;
/*
* 传输成功,进行清理、打印transferred bytes、设置env filesize/fileaddr、根据protocol决定eth_halt()
* 或 eth_halt_state_only()、设置last protocol、返回传输的字节数。
*/
case NETLOOP_SUCCESS:
net_cleanup_loop();
if (net_boot_file_size > 0) {
printf("Bytes transferred = %d (%x hex)
",
net_boot_file_size, net_boot_file_size);
env_set_hex("filesize", net_boot_file_size);
env_set_hex("fileaddr", load_addr);
}
if (protocol != NETCONS)
eth_halt();
else
eth_halt_state_only();
eth_set_last_protocol(protocol);
ret = net_boot_file_size;
debug_cond(DEBUG_INT_STATE, "--- net_loop Success!
");
goto done;
/* 失败路径,清理并返回错误(并把last protocol置为BOOTP)。 */
case NETLOOP_FAIL:
net_cleanup_loop();
/* Invalidate the last protocol */
eth_set_last_protocol(BOOTP);
debug_cond(DEBUG_INT_STATE, "--- net_loop Fail!
");
goto done;
/* 继续循环(默认) */
case NETLOOP_CONTINUE:
continue;
}
}
done:
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_KEYBOARD
net_busy_flag = 0;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CMD_TFTPPUT
/* Clear out the handlers */
net_set_udp_handler(NULL);
net_set_icmp_handler(NULL);
#endif
return ret;
}
相关文章